Causes and Risk Factors of Eczema
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, especially in families with a history of allergies or asthma. Environmental triggers such as allergens, irritants, and weather changes can exacerbate symptoms. An overactive immune response to these triggers also contributes to skin inflammation. Understanding these causes and identifying personal risk factors can help in managing eczema more effectively and preventing flare-ups.
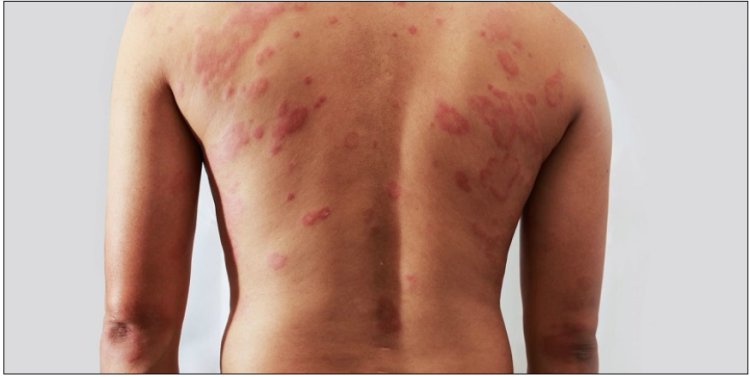
In ancient times, warriors would return from the battlefield with scars that told stories of bravery and resilience. But not all battles are fought with swords and shields. Today, millions of people, including children, wage a daily war against a relentless foe—eczema. This skin condition, characterized by red, itchy patches, can feel like a constant battle, where the body turns against itself in a seemingly endless cycle of flare-ups and relief.
This reminds me of a scene from the movie Gladiator, where the protagonist Maximus, played by Russell Crowe, bears scars from numerous battles. But unlike the visible scars of a gladiator, eczema leaves its mark in ways that aren’t always visible to others. It’s a chronic condition that can impact not just the skin but also the emotional and mental well-being of those affected.
Understanding what causes eczema is like understanding the many factors that determine the outcome of a battle. It’s not just one thing that leads to victory or defeat—it's a combination of forces. Similarly, eczema is influenced by a blend of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. By exploring these causes and identifying personal risk factors, we can better equip ourselves to manage eczema and reduce its impact on our lives.
My name is Chrysantus Shem, and with 35 years of experience in medical practice, I’ve seen firsthand how understanding the causes of a condition like eczema can lead to better management and improved quality of life. As the World Health Organization aptly stated, "Health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity." Together, let's dive into the intricacies of eczema, understand its causes, and explore how we can mitigate its effects.
Have you or someone you know battled with eczema? What do you think are the most challenging aspects of managing it? Let’s explore this together, and please share your thoughts in the comments below.
Key Objectives of the Article
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of eczema by addressing the following key objectives:
- Understand the Importance of the Topic: We'll explore why understanding the causes and risk factors of eczema is crucial for those affected.
- Identify Key Issues: We'll delve into the genetic, environmental, and immune-related factors that contribute to eczema.
- Explore Solutions: We'll discuss strategies for managing these causes and mitigating the risks.
- Provide Actionable Advice: We'll offer practical tips that can be easily implemented to reduce the impact of eczema.
- Encourage Further Learning: Finally, we'll suggest resources for those who want to deepen their understanding of eczema.
Are you ready to embark on this journey? Let’s move on to our first segment.
Understanding the Importance of Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is more than just a skin condition; it’s a chronic battle that affects millions of people worldwide. But what exactly is eczema? In simple terms, eczema is a condition that makes your skin red and itchy. It’s common in children, but it can occur at any age. It’s long-lasting (chronic) and tends to flare periodically, especially in response to certain triggers.
According to the National Eczema Association, about 31.6 million people in the United States have some form of eczema. That's nearly 10% of the population! But it’s not just about the numbers; it’s about the impact on daily life. Eczema can cause significant discomfort, disrupt sleep, and lead to emotional distress due to its visible nature. Imagine having an itch that you just can’t scratch—it’s not only frustrating but can also affect your ability to concentrate and perform daily tasks.
Eczema is often linked with other allergic conditions such as asthma and hay fever, making it a part of what’s known as the "atopic triad." If you or your child has eczema, there's a higher chance of also developing asthma or hay fever. This interconnectedness of conditions makes understanding eczema even more crucial.
But what causes eczema? Why does it flare up in some people but not in others? The answers lie in a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Understanding these causes is the first step toward managing eczema effectively.
Do you think it's easy to manage eczema every day? What strategies have you found helpful? Let’s dig deeper into what triggers this condition.
Identifying the Causes and Risk Factors of Eczema
Genetic Factors
Let's start with genetics—the foundation of who we are. Have you ever wondered why some families seem more prone to certain conditions? Genetics can hold the key. Eczema, like many other chronic conditions, has a strong genetic component. If you have a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever, you’re more likely to develop eczema yourself.
A study published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology revealed that mutations in the FLG gene, which produces a protein called filaggrin, are closely linked to the development of eczema. Filaggrin plays a crucial role in maintaining the skin's barrier function. When this barrier is compromised, it makes the skin more susceptible to irritants, allergens, and infections, leading to the dry, scaly patches characteristic of eczema.
But genetics isn’t the whole story. Not everyone with a family history of eczema will develop the condition, and not everyone with eczema has a family history. This suggests that other factors, such as the environment and immune system, also play a significant role.
What do you think about the role of genetics in eczema? Does your family history align with this?
Environmental Triggers
Imagine living in a world where your surroundings constantly challenge your skin’s defenses. For those with eczema, this is a daily reality. Environmental factors are a significant trigger for eczema flare-ups. These triggers can include anything from weather changes to exposure to allergens like dust mites, pet dander, and pollen.
One of the most common environmental triggers is dry air, especially during the winter months. When the air is dry, the skin loses moisture more easily, which can lead to an increase in eczema symptoms. Similarly, extreme heat can cause sweating, which may irritate the skin and lead to a flare-up.
Chemical irritants, such as soaps, detergents, and even certain fabrics, can also exacerbate eczema. Have you ever noticed your skin getting itchy after using a new soap or wearing certain clothes? That’s because these products can strip the skin of its natural oils, weakening its barrier and making it more susceptible to irritation.
Diet can also play a role in triggering eczema, especially in children. Common food allergens such as dairy, nuts, and eggs have been linked to eczema flare-ups in some individuals. However, it’s essential to approach dietary changes cautiously and under medical supervision, as eliminating foods without proper guidance can lead to nutritional deficiencies.
Living with eczema means being constantly aware of your environment. It’s like walking through a minefield, where any step could trigger a flare-up. But with careful management, these triggers can be minimized.
What environmental factors have you found to be the most challenging to manage with eczema?
Immune System Dysfunction
The immune system is like a well-trained army, ready to defend the body against invaders. But what happens when this army goes rogue and starts attacking its own people? In the case of eczema, the immune system can become overactive, responding too aggressively to everyday substances that are usually harmless, like pollen or pet dander.
This overreaction causes inflammation in the skin, leading to the redness, itching, and swelling that are hallmarks of eczema. It’s as if the body is in a constant state of alert, responding to threats that aren’t really there.
This dysfunction is part of what makes eczema a chronic condition. Even when the skin appears to be healthy, the immune system is still on high alert, ready to react at the slightest provocation. This is why managing eczema isn’t just about treating the skin; it’s also about calming the immune system.
Various studies have shown that people with eczema often have elevated levels of certain immune cells, known as T-helper cells, which are involved in allergic reactions. This indicates that eczema isn’t just a skin condition but also an immune system disorder.
Have you ever wondered why your eczema flares up even when you’re careful about avoiding triggers? It might be because your immune system is still in overdrive, ready to react to even the smallest irritant.
Exploring Solutions for Eczema Management
Understanding the causes of eczema is only half the battle; the other half is managing the condition effectively. The good news is that while there’s no cure for eczema, there are several strategies you can employ to reduce flare-ups and improve your quality of life.
Medical Treatments
The first line of defense in managing eczema is often medical treatment. Topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching. These creams or ointments are applied directly to the affected areas and can provide quick relief during flare-ups. However, long-term use can lead to side effects, so it’s important to use them under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
In more severe cases, systemic treatments such as oral corticosteroids or biologics may be necessary. These medications work throughout the body to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation. However, they come with a higher risk of side effects and are usually reserved for cases where other treatments have failed.
Phototherapy, or light therapy, is another option for those with moderate to severe eczema. This treatment involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial UV light, which can help reduce inflammation and improve skin symptoms. Phototherapy is often used in combination with other treatments for better results.
But medical treatments are just one piece of the puzzle. Managing eczema effectively often requires a holistic approach that includes lifestyle changes and alternative therapies.
What medical treatments have you tried for eczema?
Lifestyle Changes
While medical treatments can provide relief, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing eczema and preventing flare-ups. These changes focus on minimizing exposure to triggers, improving skin health, and reducing stress.
1. Skin Care Routine: Developing a consistent and gentle skincare routine is vital for anyone with eczema. This routine should include:
- Moisturizing Regularly: The cornerstone of eczema management is keeping the skin well-moisturized. Moisturizers help restore the skin’s barrier function, preventing moisture loss and protecting against irritants. It’s best to apply a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer immediately after bathing when the skin is still damp. Products that contain ceramides, which help repair the skin barrier, are particularly beneficial.
- Bathing Practices: When it comes to bathing, less is often more. Long, hot showers can strip the skin of its natural oils, so it’s better to take short, lukewarm showers instead. Adding colloidal oatmeal or baking soda to the bathwater can soothe itching. After bathing, gently pat the skin dry with a soft towel—don’t rub—and apply moisturizer right away.
- Avoiding Irritants: Common household products like soaps, detergents, and cleaning supplies can irritate sensitive skin. Choosing products labeled “hypoallergenic” or “for sensitive skin” can help. Additionally, wearing soft, breathable fabrics like cotton instead of wool or synthetic fibers can reduce irritation.
2. Stress Management: Stress is a known trigger for eczema flare-ups. The body’s response to stress can exacerbate inflammation, leading to a vicious cycle of itching and scratching. Incorporating stress-reducing activities into your daily routine can make a significant difference. Practices such as yoga, meditation, deep-breathing exercises, and even simple hobbies like reading or walking can help manage stress levels.
3. Diet and Hydration: For some people, certain foods can trigger eczema flare-ups. While there’s no one-size-fits-all eczema diet, keeping a food diary can help identify potential triggers. Common culprits include dairy, nuts, and gluten. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before making any significant dietary changes. Staying well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water is also important, as hydration supports overall skin health.
Have you tried any of these lifestyle changes? Which have you found to be the most effective in managing your eczema?
Alternative Therapies
In addition to conventional medical treatments and lifestyle changes, some people with eczema explore alternative therapies. While the effectiveness of these treatments varies, they can be a valuable part of a holistic approach to eczema management.
1. Acupuncture: Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to balance the flow of energy, or "Qi." Some studies suggest that acupuncture may help reduce itching and inflammation in people with eczema by modulating immune responses and improving skin barrier function. Although more research is needed, many individuals report relief from symptoms through regular acupuncture sessions.
2. Herbal Remedies: Various herbal remedies have been used traditionally to treat eczema. For example, chamomile and calendula are known for their anti-inflammatory and soothing properties. Applying creams or ointments containing these herbs may help reduce itching and redness. However, it’s important to be cautious with herbal treatments, as they can sometimes cause allergic reactions or interact with other medications.
3. Probiotics: The health of our gut microbiome—the community of microorganisms living in our digestive tract—can influence our overall health, including skin conditions like eczema. Some studies have found that taking probiotic supplements, which contain beneficial bacteria, may help reduce the severity of eczema symptoms, particularly in children. However, more research is needed to determine the effectiveness of probiotics for eczema, and it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
4. Wet Wrap Therapy: Wet wrap therapy involves wrapping the affected skin with damp bandages after applying a moisturizer or topical medication. This method helps to lock in moisture and allows the skin to absorb treatments more effectively. Wet wraps can be particularly beneficial during severe flare-ups, providing relief from intense itching and inflammation.
5. Essential Oils: Some people find relief from eczema symptoms through the use of essential oils, such as tea tree oil or lavender oil. These oils are believed to have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. However, essential oils must be used with caution, as they can be potent and may cause skin irritation if not properly diluted.
Have you explored any alternative therapies for eczema? What has been your experience with them?
Providing Actionable Advice for Managing Eczema
Now that we've covered the causes, risk factors, and various management strategies for eczema, let’s focus on some actionable advice that you can implement in your daily life. These tips are designed to help you manage eczema more effectively and prevent flare-ups.
1. Keep a Trigger Diary
One of the most effective ways to manage eczema is by identifying and avoiding triggers. Keeping a trigger diary can help you pinpoint the environmental factors, foods, or activities that lead to flare-ups. Record what you eat, the products you use, and any changes in your environment, along with notes on how your skin reacts. Over time, patterns may emerge, allowing you to take proactive steps to avoid these triggers.
2. Moisturize, Moisturize, Moisturize
Consistent and regular moisturizing is key to managing eczema. Make it a habit to moisturize your skin at least twice a day, using a product that is free from fragrances and harsh chemicals. Always carry a small bottle of moisturizer with you, so you can reapply throughout the day if needed, especially after washing your hands or being in dry environments.
3. Choose Clothing Wisely
The clothes you wear can have a significant impact on your skin’s condition. Opt for soft, breathable fabrics like cotton and avoid tight-fitting clothes that can rub against your skin. It’s also a good idea to wash new clothes before wearing them to remove any chemicals or dyes that could irritate your skin. When doing laundry, use a gentle, fragrance-free detergent, and consider adding an extra rinse cycle to ensure all detergent is removed.
4. Stay Hydrated
Hydration is essential for healthy skin. Make sure you drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially if you live in a dry climate or are physically active. Drinking water helps to keep your skin hydrated from the inside out, supporting its natural barrier function.
5. Be Gentle with Your Skin
Your skin is more sensitive than most, so it’s important to treat it with care. Avoid scrubbing your skin too hard, whether you’re bathing or toweling off. Use a gentle cleanser that doesn’t strip your skin of its natural oils, and avoid hot water, which can exacerbate dryness. When drying your skin, pat it gently with a soft towel rather than rubbing.
6. Manage Stress
Since stress is a known trigger for eczema, finding ways to manage it is crucial. Engage in activities that help you relax, whether it’s through mindfulness practices, exercise, or spending time with loved ones. Even small changes, like taking a few deep breaths when you feel stressed, can make a difference in managing eczema symptoms.
What tips do you find most useful? Have you developed your own strategies for managing eczema? Share them in the comments!
Encourage Further Learning
Managing eczema is a journey, and understanding the condition is a key part of that journey. But there's always more to learn, and the more you know, the better equipped you'll be to manage your symptoms and live comfortably.
Here are some resources to help you continue your learning:
- National Eczema Association - A comprehensive resource for everything related to eczema, including the latest research, treatment options, and patient stories.
- American Academy of Dermatology - Offers detailed information on eczema, including treatment guidelines and tips for managing symptoms.
- WebMD’s Eczema Guide - Provides easy-to-understand information on eczema causes, symptoms, and treatments. Check it out at WebMD Eczema Guide.
- Eczema Outreach Support - A charity that offers support and resources for families dealing with eczema.
- Books on Eczema - Consider reading books like The Eczema Diet by Karen Fischer, which offers dietary advice for managing eczema, or Eczema-Free for Life by Adnan Nasir, which provides insights into long-term management strategies.
Continuing your education on eczema not only empowers you but also enables you to make informed decisions about your health. Have you found any other helpful resources? Let me know in the comments!
Conclusion
Eczema is a complex condition influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. While there is no cure, understanding these causes and identifying personal risk factors can significantly improve the management of eczema and reduce the frequency of flare-ups.
From adopting a consistent skincare routine to exploring alternative therapies, there are various strategies available to help you manage your eczema effectively. Remember, each person’s experience with eczema is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized management plan that meets your specific needs.
As you continue your journey with eczema, stay informed, stay proactive, and stay connected with others who share similar experiences. Managing eczema is a marathon, not a sprint, and every step you take brings you closer to a better quality of life.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Millions of people around the world are dealing with eczema, and there is a wealth of knowledge, support, and resources available to help you manage this condition. Whether it's through medical treatments, lifestyle changes, or simply sharing your experiences with others, every effort counts.
As we wrap up, I encourage you to think about the one change you can make today to better manage your eczema. Whether it's switching to a new moisturizer, reducing stress, or even reaching out to a support group, small steps can lead to significant improvements over time.
Thank you for joining me on this exploration of the causes and risk factors of eczema. I hope you found the information helpful and empowering. If you have any questions, experiences to share, or tips that have worked for you, please don't hesitate to leave a comment below. Your insights could help others who are going through similar challenges.
And don’t forget to subscribe to NourishNetBlog.com to stay updated with the latest articles, tips, and resources for managing eczema and other health-related topics. Together, we can navigate the complexities of eczema and strive for healthier, happier skin.
Resources
American Academy of Dermatology. (2019). American Academy of Dermatology | American Academy of Dermatology. Aad.org. https://www.aad.org/
EczemaOutreachSupport. (2024). Eczema support for families. Eczema Outreach Support. https://eos.org.uk/
Mayo Clinic. (2024). Mayo Clinic. Mayoclinic.org; Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. https://www.mayoclinic.org/
National Eczema Association. (2013). National Eczema Association. National Eczema Association. https://nationaleczema.org/
National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2023). National Institutes of Health (NIH). National Institutes of Health (NIH); US Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.nih.gov/
The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. (2019). Home Page: Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. Jacionline.org. https://www.jacionline.org/
Final Thoughts
Eczema is a condition that requires ongoing attention, but with the right knowledge and tools, it is possible to manage it effectively and lead a fulfilling life. I encourage you to take what you’ve learned here, apply it to your daily routine, and explore the resources provided to further your understanding.
What’s one change you’re willing to make today to improve your eczema management? Share it in the comments, and let’s keep the conversation going. Together, we can make a difference, one small step at a time.
Thank you for reading, and I look forward to hearing your thoughts!
With this article, I hope you feel more equipped to tackle eczema head-on. If you enjoyed this article and found it useful, don’t forget to check out other related topics on NourishNetBlog.com. Continue reading about managing chronic skin conditions here, and explore the impact of diet on skin health here.
Stay informed, stay healthy, and remember, you are not alone in this journey.
What's Your Reaction?




















