8 Indications Your Body Is Suffering From Inflammation
Inflammation is a silent saboteur. Stay alert to these eight indications that your body might be experiencing an inflammatory response.
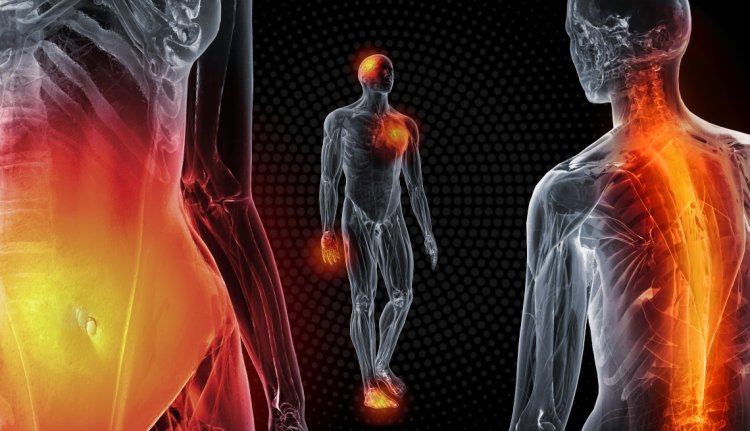
Imagine you wake up one morning feeling not quite yourself. You can't put your finger on it, but something feels off. You're not sick, exactly, but you're definitely not at your best. This story is all too familiar to many of us, and it's often the body's subtle way of signaling that something is amiss - specifically, that you might be experiencing inflammation.
Inflammation is a crucial part of the body's immune response, a defense mechanism against injury or infection. However, when it becomes chronic, it can lead to a myriad of health issues, some of which are not so obvious. That's why I'm writing this article. My aim is to shed light on the often-overlooked signs of inflammation within our bodies, helping readers identify and address these issues before they escalate into more significant health concerns.
Let me introduce myself. I am Chrys Shem. With over two decades of Public health practice under my belt, I've dedicated my life to understanding the complexities of the human body and how to maintain its health. I share my knowledge on NourishNetBlog.com, aiming to empower others to live healthier, fuller lives. Through this article, I hope to add to that mission by guiding you on how to recognize and address inflammation in your body.
Key Objectives of this Article
In this article, we aim to achieve several important objectives to enhance your understanding of inflammation and its effects on the body. These objectives are designed not just to inform but to empower you to take charge of your health. Here’s what we’re looking to cover:
- Define Inflammation – We'll start by clarifying what inflammation is, distinguishing between its acute and chronic forms. Understanding this distinction is crucial for recognizing the body's natural response to injury and infection versus a long-term condition that could lead to health issues.
- Identify Common Causes – Next, we'll explore what commonly triggers inflammation in the body. From lifestyle factors like diet and stress to environmental influences, knowing these triggers can help in managing or preventing chronic inflammation.
- Spot the Signs – The core of our discussion will revolve around the eight signs of inflammation inside your body. These indicators can often be subtle, making them easy to overlook but crucial to recognize.
- Understand the Effects – We'll delve into how chronic inflammation can affect your health in the long term. Understanding the potential consequences can motivate us to take action towards reducing inflammation.
- Offer Practical Tips for Management and Prevention – Lastly, we'll provide actionable advice on how to manage or prevent inflammation through lifestyle adjustments, diet, and other practical measures.
By the end of this article, you'll be equipped with the knowledge to recognize signs of inflammation in your body and understand the steps you can take to mitigate its effects. This awareness is a powerful tool in maintaining and improving your health.
1. Define Inflammation
Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury or infection. It's a critical part of the immune system's defense mechanism, helping to heal damaged tissue and fend off foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses. When we talk about inflammation, it's important to differentiate between two types: acute and chronic.
Acute Inflammation is immediate and occurs shortly after an injury or when the body is fighting an infection. It's characterized by redness, heat, swelling, pain, and sometimes a loss of function in the affected area. This type of inflammation is typically short-lived, lasting a few days to a week. It's a sign that your body is actively working to heal itself.
Chronic Inflammation, on the other hand, is a longer-term response that can last for months or even years. It can arise from persistent acute inflammation or due to external factors like stress, obesity, smoking, or prolonged exposure to pollutants. Unlike acute inflammation, which is beneficial, chronic inflammation can silently contribute to the development of diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and arthritis.
The key to managing inflammation lies in recognizing when it's beneficial and when it's harmful. Acute inflammation is a necessary part of healing, but chronic inflammation is something we need to be aware of and manage for our long-term health.
Now, knowing this distinction, what do you think? How often do we overlook the signs of chronic inflammation, mistaking them for temporary discomforts or ignoring them altogether? I'd love to hear your thoughts in the comments.
2. Identify Common Causes
Understanding what triggers inflammation in the body is crucial for preventing and managing it effectively. While some causes are well-known, others might surprise you. Let’s delve into the common culprits behind inflammation:
-
Diet - Certain foods can trigger an inflammatory response. Processed foods, sugary treats, trans fats, and high intake of red meat are known to promote inflammation. On the flip side, a diet lacking in fruits, vegetables, and other anti-inflammatory foods can also contribute to increased inflammation levels.
-
Lack of Physical Activity - A sedentary lifestyle is linked to higher levels of inflammation. Regular physical activity, on the other hand, can help reduce inflammation markers in the body.
-
Stress - Chronic stress triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Over time, this can lead to sustained levels of inflammation, affecting the body’s balance and potentially leading to various health issues.
-
Obesity - Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, can produce pro-inflammatory cytokines, leading to chronic inflammation. Losing weight can help decrease these inflammatory markers.
-
Smoking - Tobacco smoke contains a plethora of chemicals that can cause inflammation throughout the body. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce inflammation levels.
-
Alcohol - Excessive alcohol consumption can damage body tissues, leading to inflammation. Moderation is key, as even small amounts can contribute to inflammation in some individuals.
-
Environmental Pollutants - Exposure to pollutants, such as air pollution and certain chemicals, can trigger inflammatory responses. Limiting exposure to these pollutants as much as possible can help reduce inflammation.
-
Chronic Infections - Persistent infections can cause long-term inflammation in the body. Managing these infections effectively is crucial for reducing inflammation.
Recognizing and addressing these triggers can significantly impact your body’s inflammatory response, promoting better health and well-being. Now, I'm curious to hear your thoughts. Have you noticed certain triggers that worsen inflammation for you? What steps have you taken to reduce these triggers in your life? Please, share your experiences in the comments.
3. Spot the Signs
Identifying the signs of inflammation in your body is crucial for taking timely action to address it. While some signs might be easy to spot, others can be quite subtle. Here are eight indicators that your body might be experiencing an inflammatory response:
-
Persistent Fatigue - Feeling unusually tired or fatigued, even after getting enough sleep, can be a sign of chronic inflammation. It's as if your body is constantly working overtime to fight an invisible battle.
-
Unexplained Pain - Chronic inflammation often manifests as pain in various parts of the body. This could be a dull ache, a throbbing pain, or a persistent discomfort without an obvious cause.
-
Digestive Issues - Inflammation can affect the gut, leading to symptoms like bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain. These signs can be mistaken for food intolerances or temporary digestive upset, but if they persist, they may indicate an inflammatory response.
-
Skin Issues - Conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and rosacea can be signs of inflammation. Inflammatory responses can cause the skin to become itchy, red, or inflamed.
-
Frequent Infections - If you find yourself getting sick more often than usual, it could be a sign that chronic inflammation is weakening your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections.
-
Weight Fluctuations - Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight can be linked to inflammation. Inflammatory responses can disrupt the body's metabolism and hormone balance, leading to weight issues.
-
Mood Disorders - Chronic inflammation has been linked to mood changes, including depression and anxiety. The brain's inflammatory response can affect neurotransmitter levels and brain function.
-
Stiffness and Swelling - Waking up with stiff joints or noticing swelling in certain areas of your body without an apparent reason can be indicative of ongoing inflammation.
Recognizing these signs is the first step toward addressing chronic inflammation. Now, what do you think? Have you ever experienced any of these symptoms and wondered about their cause?
4. Understand the Effects
Chronic inflammation acts like a slow-burning fire in the body, often silent and unnoticed until it manifests as various health conditions. Its effects can be far-reaching, impacting nearly every aspect of our health. Let's explore some of the significant consequences of long-term inflammation:
-
Heart Disease - Chronic inflammation is a key player in the development of cardiovascular diseases. It contributes to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to atherosclerosis, which can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
-
Diabetes - Inflammation affects insulin resistance, a condition in which the body's cells don't respond effectively to insulin. This can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
-
Cancer - Long-term inflammation can contribute to DNA damage and lead to the development of cancer. Inflammatory conditions in the body create an environment that can support the growth and spread of cancerous cells.
-
Neurological Diseases - Chronic inflammation is implicated in the development of neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Inflammation in the brain can lead to the degeneration of neurons, affecting memory and motor functions.
-
Autoimmune Diseases - In some cases, chronic inflammation can trigger the body's immune system to attack its own tissues, leading to autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease.
-
Mental Health - There's a growing body of evidence linking chronic inflammation to mental health issues, including depression and anxiety. The inflammatory response can affect brain chemistry and lead to changes in mood and behavior.
Understanding these effects highlights the importance of managing inflammation for our overall well-being. It's a reminder that chronic inflammation doesn't just affect one part of the body; it can influence our health in myriad ways.
5. Practical Tips for Management and Prevention
Managing and preventing inflammation is key to maintaining overall health and well-being. Here are practical steps you can take to reduce inflammation in your body:
-
Adopt an Anti-inflammatory Diet - Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Foods like berries, leafy greens, nuts, and fatty fish are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Avoid processed foods, excessive sugar, and trans fats, which can trigger inflammation.
-
Regular Exercise - Physical activity helps reduce inflammation. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. This can include walking, cycling, swimming, or any activity that you enjoy and can maintain consistently.
-
Get Enough Sleep - Quality sleep is crucial for reducing inflammation. Aim for 7-9 hours of good sleep per night. Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine to improve your sleep quality.
-
Manage Stress - Chronic stress contributes to inflammation. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, and mindfulness can help manage stress levels. Finding hobbies or activities that relax and rejuvenate you is also important.
-
Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking - Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking are known to increase inflammation. Limiting alcohol to moderate levels and quitting smoking can significantly reduce inflammation and improve your health.
-
Stay Hydrated - Adequate hydration is important for reducing inflammation. Drink plenty of water throughout the day, and limit sugary drinks and excessive caffeine.
-
Consider Anti-inflammatory Supplements - Certain supplements, including omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric, and ginger, have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement.
-
Regular Medical Check-ups - Regular visits to your healthcare provider can help catch and address signs of inflammation early. Discuss any concerns or symptoms you have with your doctor.
Implementing these tips can make a significant difference in managing and preventing chronic inflammation. Now, I'd love to hear from you. Do you have any tips or strategies that have worked for you in managing inflammation? Feel free to share your thoughts in the comments.
In our exploration of inflammation and its impact on health, we've journeyed through understanding what inflammation is, recognizing its signs, comprehending its effects on the body, and finally, learning practical tips for managing and preventing it. Chronic inflammation is a pervasive issue that can lead to a host of health problems, including heart disease, diabetes, cancer, neurological diseases, autoimmune disorders, and mental health challenges. However, armed with knowledge and actionable strategies, we can take steps to mitigate inflammation and promote our overall well-being.
Editor's Summary:
-
Understanding Inflammation: Inflammation is the body's defense mechanism against injury and infection, but when it becomes chronic, it poses significant health risks.
-
Recognizing the Signs: Key indicators of inflammation include persistent fatigue, unexplained pain, digestive issues, skin problems, frequent infections, weight fluctuations, mood disorders, and stiffness or swelling in the body.
-
Comprehending the Effects: Chronic inflammation can lead to serious health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, cancer, neurological disorders, autoimmune diseases, and mental health issues.
-
Practical Management and Prevention Tips: Reducing inflammation involves adopting a healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, staying active, managing stress, ensuring adequate sleep, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying hydrated.
In conclusion, awareness and proactive management of inflammation can significantly improve your health and quality of life. As we close this discussion, I encourage you to reflect on your lifestyle and consider implementing some of the tips we've shared. Remember, taking small steps towards reducing inflammation can lead to big changes in your health.
Join our movement towards a healthier life by subscribing to our NourishNetBlog.com, where we continue to share insights and tips for living well. Together, we can make informed choices that enhance our health and well-being.
Resources:
https://www.healthline.com/health/chronic-inflammation
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/248423
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21660-inflammation
What's Your Reaction?




















