8 Signs of Inflammation Inside Your Body to Recognize
Uncover the 8 subtle signs of inflammation and learn how to manage this common health issue. Explore our expert tips for reducing inflammation naturally.
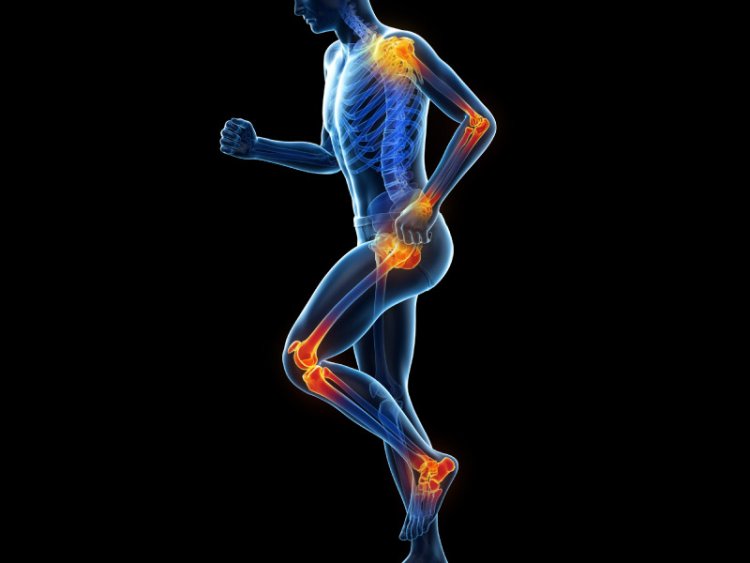
Sometimes have you wondered whether there is a silent battle raging within, unseen yet palpable, as your body's defenses mobilize against unseen foes? Inflammation, the body's intricate response to injury or infection, manifests in myriad ways, whispering subtle hints of its presence. From the faint throb of joint pain to the fiery flush of inflamed skin, these signs serve as cryptic clues, urging us to heed the whispers of our body's inner turmoil. Join us as we embark on a journey to unravel the complex language of inflammation, empowering you to recognize its subtle cues and take proactive steps toward restoring balance and vitality within.
Inflammation is a natural and essential part of the body's immune response to injury, infection, or irritation. It is a complex biological process that involves the activation of the immune system to remove harmful stimuli, initiate tissue repair, and restore homeostasis. When the body detects a threat, such as pathogens or damaged cells, it releases inflammatory mediators, including cytokines, chemokines, and prostaglandins, which trigger a cascade of events leading to the characteristic signs of inflammation: redness, swelling, heat, pain, and loss of function.
Inflammation inside our bodies refers to the presence of this immune response within internal tissues, organs, or systems. While inflammation is a necessary defense mechanism for fighting off infections and promoting healing, chronic or excessive inflammation can have detrimental effects on health and contribute to the development and progression of various chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and cancer.
The prevalence of inflammation is widespread, with research indicating that chronic low-grade inflammation is increasingly recognized as a common underlying factor in many chronic health conditions. Factors such as diet, lifestyle, environmental exposures, genetics, and aging can influence the risk of inflammation.
Age is a significant determinant of inflammation, as the body's immune system changes over time. While acute inflammation is generally more robust in younger individuals, chronic inflammation tends to become more prevalent with advancing age. Older adults may experience higher levels of inflammatory markers in their blood and tissues, contributing to age-related diseases and declining health.
In terms of gender differences, research suggests that inflammatory responses may vary between males and females due to hormonal differences and genetic factors. Women, for example, may experience fluctuations in inflammatory markers during menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and menopause, which can influence the risk of inflammatory diseases. Additionally, some studies have found that certain inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, may be more common in women than in men.
Certain demographic groups may be more susceptible to inflammation due to socioeconomic factors, environmental exposures, and underlying health conditions. For example, individuals with obesity, metabolic syndrome, or chronic stress may have higher levels of inflammation due to systemic dysregulation of the immune system.
It is crucial for individuals to be aware of the signs of inflammation and to recognize when inflammation becomes chronic or excessive. Chronic inflammation often presents with subtle symptoms that may be overlooked or attributed to other causes, but persistent symptoms such as fatigue, joint pain, digestive issues, skin problems, and recurrent infections may indicate underlying inflammation. By recognizing these signs and addressing inflammation early, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk of chronic disease, improve their overall health and well-being, and enhance their quality of life.
Also Read: The Future of Arthritis Treatment
In this article, we're going to unravel the mysteries of inflammation. Inflammation is like the body's own emergency response system. It's a necessary process for healing, but when it goes into overdrive, it can signal or exacerbate various health issues. The challenge lies in recognizing the subtleties of this internal alarm to address it promptly and effectively.
"Chronic inflammation acts like a slow-burning fire, contributing to the development of several diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and Alzheimer's," notes Dr. Susan Blum, a pioneer in functional medicine. The World Health Organization underscores this, indicating that chronic diseases linked to inflammation are predominant causes of death worldwide.
This article aims not just to inform but to empower you. With insights rooted in scientific research and real-life observations, we'll explore the signs of inflammation that are often overlooked. Remember, knowledge is the first step toward action.
What do you think about the importance of recognizing these inflammation signs? Feel free to share your thoughts in the comments below.
Key Objectives of this Article
In delving into the realm of inflammation, our mission is to equip you with the knowledge to identify its signs and understand its implications. Here are the five key objectives this article aims to achieve:
- Understanding Inflammation: We'll start by demystifying what inflammation is and why it occurs. It's crucial to distinguish between acute inflammation, a healthy response to injury or infection, and chronic inflammation, which can undermine your health.
- Recognizing the Signs: Identifying the eight signs of inflammation lurking within the body is our primary goal. These indications can be subtle, often masquerading as general discomfort or minor health nuisances, making them easy to overlook.
- Linking Inflammation to Chronic Diseases: We'll explore how chronic inflammation serves as a common thread among various diseases. By connecting the dots between inflammation and conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders, we underscore the urgency of addressing inflammation.
- Prevention and Management Strategies: Knowledge alone isn't enough; application is key. We'll provide practical strategies for preventing and managing inflammation through lifestyle and dietary adjustments.
- Empowering Self-Care: Lastly, we aim to empower you with self-care practices that mitigate inflammation. By incorporating simple yet effective habits into your daily routine, you can significantly enhance your body's resilience against inflammation.
With these objectives in mind, we set the stage for a comprehensive exploration of inflammation and its impact on our health. Let's embark on this journey together, fostering a deeper understanding and actionable insights.
Do you think these objectives cover the essential aspects of inflammation? I'd love to hear your thoughts in the comments below.
Understanding Inflammation
Inflammation is a term that often conjures images of swollen ankles after a sprain or the redness surrounding a cut. Indeed, this is the body's immediate reaction to harm—acute inflammation—a necessary part of healing. However, there's another side to the story: chronic inflammation, a stealthy and prolonged response that can play a significant role in various diseases.
What Is Inflammation?
In essence, inflammation is the body's defense mechanism. When confronted with an invader, such as bacteria, toxins, or trauma, the immune system springs into action. Chemicals from white blood cells are released into the bloodstream or affected tissues to protect the body. This increases blood flow to the area, causing redness and warmth. Some of the chemicals cause fluid to leak into tissues, resulting in swelling.
Acute vs. Chronic Inflammation
Acute inflammation is short-lived, typically lasting a few days. If the cause of inflammation isn't resolved, it can transition into a chronic phase, silently persisting for months or even years. Chronic inflammation is where the trouble begins. Unlike its acute counterpart, chronic inflammation can slowly damage the body's cells, tissues, and organs, setting the stage for various health issues.
The Silent Saboteur
Chronic inflammation is insidious. It can quietly simmer in the body without any overt symptoms. Over time, this type of inflammation can contribute to the development and progression of several diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) states that chronic diseases are the leading cause of death and disability in the United States, with many having links to chronic inflammation.
Also Read: 8 Chronic Inflammation Symptoms That Shouldn't Be Overlooked
"Many major diseases that plague us—including cancer, heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, depression, and Alzheimer's—have been linked to chronic inflammation," says Dr. Brent Bauer of the Mayo Clinic. It's a clear indicator of how crucial it is to manage inflammation for our overall health.
Key Takeaway
Understanding inflammation is foundational to recognizing its impact on our well-being. It's a double-edged sword: beneficial in the short term as part of the healing process but potentially harmful when it becomes chronic. This distinction is critical in our journey to recognize the signs and mitigate the risks associated with prolonged inflammation.
What are your thoughts on the role of inflammation in health and disease? Engage with us in the comments section below.
Recognizing the Signs
Identifying the signs of chronic inflammation is crucial, as it often operates under the radar, manifesting in ways that are easy to dismiss or misinterpret. Here are eight subtle yet significant signs your body might be experiencing an inflammatory response:
- Persistent Fatigue: Unlike the normal ebb and flow of energy levels, chronic inflammation can lead to unrelenting tiredness that isn't alleviated by rest. This type of fatigue can impact daily functioning and is often overlooked as a sign of inflammation.
- Joint Pain or Stiffness: Chronic inflammation can affect the joints, leading to pain or stiffness that doesn't originate from a clear injury. It may be mistaken for signs of aging or overexertion but could indicate an inflammatory response.
- Gut Health Issues: The gut is a significant indicator of health, and issues such as bloating, constipation, diarrhea, or abdominal pain can signal inflammation. The gastrointestinal tract houses a substantial part of the immune system, and its distress can reflect underlying inflammation.
- Skin Problems: Skin conditions such as rashes, eczema, or psoriasis are not just surface-level concerns. They can be manifestations of the body's inflammatory response, signaling an imbalance or irritation beneath the skin.
- Gum Disease: Often overlooked, gum disease or periodontitis is an inflammatory condition. Swollen, red, or bleeding gums can be a visible marker of chronic inflammation in the body.
- Mood Disorders: The link between chronic inflammation and mood disorders like depression and anxiety is increasingly recognized. Inflammatory markers are often elevated in individuals experiencing these conditions, suggesting an underlying biological connection.
- High Blood Pressure and Heart Conditions: Chronic inflammation can contribute to the development of plaque in the arteries, leading to high blood pressure and increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Unexplained Weight Changes: Weight gain, especially around the abdominal area, or difficulty losing weight can be associated with inflammation. Adipose tissue (fat cells) can produce inflammatory markers, contributing to a cycle of weight gain and inflammation.
Recognizing these signs is a vital step in addressing potential inflammation. By being attentive to these indicators, individuals can take proactive measures to manage inflammation through lifestyle changes and medical consultation.
Also Read: 7 Unexpected Advantages of Staying Physically Active
In the vast sea of health concerns, chronic inflammation is a lurking undercurrent, influencing numerous conditions and overall well-being. As we move forward, we'll explore the connections between chronic inflammation and specific diseases, shedding light on the critical role of inflammation in health and disease.
Have you or someone you know experienced these signs of inflammation? What was the journey like in recognizing and addressing them? Share your experiences in the comments section.
Linking Inflammation to Chronic Diseases
The stealthy nature of chronic inflammation makes it a pervasive risk factor for several chronic diseases. Its role in the development and progression of these conditions cannot be overstated. Let's delve into how chronic inflammation is intricately linked to some of the most common chronic diseases.
Heart Disease: Chronic inflammation is a key player in the development of cardiovascular diseases. It contributes to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. This plaque buildup can lead to heart attacks and strokes. The American Heart Association highlights inflammation's role in heart disease, emphasizing the importance of managing inflammation to protect heart health.
Diabetes: Inflammation and diabetes are closely related. Chronic inflammation can lead to insulin resistance, where the body's cells don't respond effectively to insulin. This resistance is a precursor to type 2 diabetes, as it impairs the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels. The link between inflammation and diabetes underscores the need for anti-inflammatory lifestyle changes to prevent or manage the condition.
Autoimmune Diseases: Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's tissues, often fueled by chronic inflammation. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis are associated with an overactive inflammatory response, highlighting the need to manage inflammation in autoimmune disorders.
Cancer: Chronic inflammation has been identified as a contributing factor to the development of certain types of cancer. Inflammation can cause DNA damage, leading to mutations and the potential for cancerous growth. Reducing inflammation is a key strategy in cancer prevention and management.
Obesity: Obesity and inflammation are interlinked, with excess body fat contributing to an inflammatory state in the body. This inflammation can exacerbate the risk of developing other inflammation-related diseases, creating a vicious cycle of health complications.
Chronic Kidney Disease: Inflammation plays a role in the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD), affecting the kidneys' ability to filter blood effectively. Managing inflammation is critical in slowing the progression of CKD and maintaining kidney health.
Understanding these links between chronic inflammation and various diseases emphasizes the importance of early detection and management of inflammation. By addressing inflammation, we can significantly impact the prevention and management of these chronic conditions.
As we explore the intricacies of inflammation and its far-reaching effects, it's clear that a proactive approach to managing inflammation can be a game-changer for our health.
Also Read: 6 Early Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
What's your take on the link between inflammation and chronic diseases? Do you see the potential for lifestyle changes to make a significant impact? I encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Given the substantial role chronic inflammation plays in various diseases, adopting strategies to prevent and manage it is essential for maintaining health and well-being. Here are actionable steps you can take:
- Adopt an Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Nutrition plays a pivotal role in managing inflammation. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Incorporate a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your diet. On the flip side, try to minimize the intake of processed foods, sugars, and trans fats, which can fuel inflammation.
- Regular Physical Activity: Exercise is a powerful anti-inflammatory agent. Engaging in moderate exercise for at least 150 minutes a week can help reduce inflammation. Activities can range from walking and swimming to cycling and strength training. The key is consistency and finding an activity you enjoy.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, can increase inflammation. Working towards and maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can significantly reduce inflammation levels.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can trigger and exacerbate inflammation. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or spending time in nature can help manage stress levels and reduce inflammation.
- Get Enough Sleep: Quality sleep is crucial for reducing inflammation. Aim for 7-9 hours of good-quality sleep per night. Establishing a regular sleep schedule and creating a restful environment can improve sleep quality.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase inflammation and damage your body. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can have profound health benefits.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Routine health screenings can help detect early signs of inflammation and prevent chronic diseases. Discussing your concerns about inflammation with a healthcare provider can lead to personalized advice and interventions.
By implementing these strategies, you can take proactive steps toward managing inflammation and improving your overall health. It's about making consistent, mindful choices that support your body's well-being.
Adopting an anti-inflammatory lifestyle doesn't have to be overwhelming. Start with small changes and gradually incorporate more as you feel comfortable. Every step towards reducing inflammation is a step towards a healthier life.
What do you think about these strategies? Have you tried any of them, and did you notice a difference in how you feel? Share your experiences and thoughts in the comments below.
Practical Tips in List & Short Description Format
To further empower you in your journey to manage and reduce inflammation, here are practical tips that you can easily integrate into your daily routine:
- Start Your Day with Anti-inflammatory Foods: Begin with a breakfast that includes turmeric, ginger, or berries. These foods are known for their potent anti-inflammatory properties.
- Incorporate Physical Activity into Your Day: Take short walks during breaks, use the stairs instead of the elevator, or have a mini workout session at home. Small increments of physical activity throughout the day add up.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water is essential for flushing toxins out of your body, which can help reduce inflammation. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day.
- Practice Mindfulness or Meditation: Even just a few minutes of mindfulness or meditation can significantly reduce stress, a known contributor to inflammation.
- Opt for Whole Grains: Swap out refined carbohydrates with whole grains like oats, quinoa, and brown rice. Whole grains contain more fiber and nutrients, which can help reduce inflammation.
- Increase Your Intake of Antioxidants: Eat a rainbow of fruits and vegetables to get a wide range of antioxidants, which can neutralize free radicals and reduce inflammation.
- Limit Processed Foods and Sugar: Processed foods and high sugar intake can spike inflammation. Opt for natural, whole foods as much as possible.
- Get Quality Sleep: Establish a soothing nighttime routine and aim to go to bed and wake up at the same time each day to ensure you're getting restorative sleep.
- Connect with Others: Social connections can improve your mood and help manage stress. Whether it's a phone call with a friend or a family dinner, staying connected is important.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body responds to different foods, activities, and stress levels. Tailoring your lifestyle to what makes you feel best is key to managing inflammation.
Understanding and managing inflammation is crucial for maintaining health and preventing chronic diseases. By recognizing the signs of inflammation and taking steps to address it through lifestyle and dietary changes, we can significantly improve our quality of life.
Also Read: 8 Indications Your Body Is Suffering From Inflammation
Remember, the journey to better health is a marathon, not a sprint. Small, consistent changes can have a profound impact over time. I encourage you to experiment with the strategies and tips shared in this article and find what works best for you.
I hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into inflammation and its impact on your health. Your body's subtle cries for help, in the form of inflammation, should not be ignored. By staying alert and proactive, you can navigate your way to a healthier, more vibrant life.
What will be your first step towards addressing inflammation? I'm eager to hear your plans and thoughts. Share them in the comments section below. And don't forget to subscribe to our blog at NourishNetBlog.com to continue your journey toward better health. Together, let's embrace a lifestyle that nourishes and protects our well-being.
Resources
To support your journey in understanding and managing inflammation, here are several reputable sources and further readings. These resources provide in-depth information on inflammation, its impact on health, and strategies for prevention and management:
What's Your Reaction?




















