Causes and Risk Factors of Rosacea
Rosacea is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, especially in families with a history of rosacea or other skin conditions. Environmental triggers such as sun exposure, stress, and certain foods can exacerbate symptoms. An overactive immune response to these triggers leads to inflammation and visible blood vessels. Understanding these causes and identifying personal risk factors can help in managing rosacea more effectively and preventing flare-ups
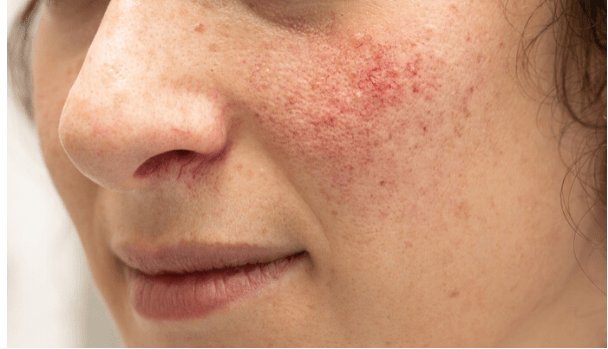
Have you ever seen a person in a TV show or a movie with a constantly flushed face, leading you to wonder what might be causing it? Perhaps you've watched a show like Grey's Anatomy where a character's unexplained facial redness is suddenly brought into focus. Or maybe you've seen images of celebrities like Bill Clinton or Princess Diana who were known to struggle with facial redness and wondered why that was.
These visible symptoms are often signs of a common yet misunderstood condition called rosacea. Despite affecting millions of people worldwide, the exact causes of rosacea remain a bit of a mystery to many. However, what we do know is that rosacea isn't just about having rosy cheeks. It's a chronic skin condition that can lead to significant discomfort and, if left unmanaged, can worsen over time.
My name is Dr. Chrysantus Shem, and with over 35 years of experience in dermatology, I've seen firsthand how the complexities of rosacea can impact individuals not just physically but emotionally as well. This article is dedicated to exploring the various causes and risk factors associated with rosacea. We'll delve into the genetic, environmental, and immune-related factors that contribute to this condition, shedding light on how these elements intertwine to trigger and exacerbate symptoms.
According to the National Rosacea Society, approximately 16 million Americans are affected by rosacea, though many remain undiagnosed. While the condition is more commonly seen in fair-skinned individuals, it can affect anyone, regardless of skin color or ethnicity. The multifaceted nature of rosacea means that its causes are not always clear-cut, and managing it effectively requires a nuanced understanding of its triggers and contributing factors.
But before we dive deep into these aspects, I'd love to hear from you. Have you or someone you know experienced symptoms of rosacea? What has your experience been like? Feel free to share your thoughts in the comments below as we journey through this topic together.
Key Objectives of the Article:
- Identify the Genetic and Environmental Factors Contributing to Rosacea: We'll explore how your genes and the environment around you play a crucial role in the development of rosacea.
- Discuss the Role of the Immune System in Rosacea Development: Learn how your body's immune system might be overreacting to certain triggers, leading to inflammation and other rosacea symptoms.
- Highlight Common Risk Factors: From lifestyle habits to physical conditions, we'll break down the most common risk factors that could be putting you at a higher risk of developing rosacea.
Do you think these objectives cover what you're looking for? Should we move on to the next segment?
What Is Rosacea? Why Is It Important to Understand?
Rosacea is more than just an occasional blush; it's a chronic condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, visible blood vessels, and, in some cases, acne-like bumps. For many, the symptoms can come and go, with periods of flare-ups followed by remission. However, without proper management, the condition can progressively worsen over time, leading to persistent redness, thickening of the skin, and, in severe cases, swelling of the nose (a condition known as rhinophyma).
Understanding rosacea is crucial because it helps individuals recognize the early signs and take proactive steps to manage the condition before it escalates. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, about half of the people diagnosed with rosacea experience eye problems, such as dryness, irritation, and swollen, reddened eyelids. This highlights the importance of not just treating the skin but also monitoring other potential symptoms.
You might be wondering: what exactly causes this condition? Is it something you inherit from your parents, or is it more about the environment you live in? Let’s explore these questions in detail.
Genetic Factors: Is Rosacea in Your Genes?
One of the primary questions many patients ask is whether rosacea is inherited. The short answer is, yes, genetics can play a significant role in the development of rosacea. If you have a family history of the condition, you are more likely to develop it yourself. A study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found that over 30% of people with rosacea reported having a relative with the same condition
The genetic predisposition to rosacea is often linked to certain skin types. Individuals with fair skin, particularly those of Celtic or Northern European descent, are more prone to developing the condition. This doesn’t mean that people with darker skin tones are immune, but they are less likely to be affected. It’s also worth noting that rosacea tends to be more prevalent in women than men, though men who do develop the condition often experience more severe symptoms.
Interestingly, while the exact genes responsible for rosacea haven’t been fully identified, researchers believe that a combination of genetic factors related to skin sensitivity and immune system function may be at play. This brings us to our next segment: the role of the immune system.
Do you have a family history of skin conditions like rosacea? How do you think this has influenced your own skin health? I'd love to hear your thoughts!
Environmental Triggers: What External Factors Worsen Rosacea?
While genetics lay the groundwork for rosacea, environmental factors often act as the trigger that brings the condition to the surface. Common environmental triggers include sun exposure, extreme temperatures, wind, and certain skincare products. These factors can aggravate the skin, leading to the dilation of blood vessels and inflammation, which are hallmarks of rosacea.
For example, exposure to sunlight is one of the most frequently reported triggers for rosacea flare-ups. According to the National Rosacea Society, up to 81% of people with rosacea identify sun exposure as a trigger for their symptoms. This makes protecting your skin from the sun’s harmful rays not just a cosmetic concern, but a vital step in managing the condition.
Moreover, lifestyle factors such as stress, alcohol consumption, and diet can also contribute to flare-ups. Spicy foods, hot beverages, and alcohol—particularly red wine—are notorious for triggering symptoms in many rosacea patients. The key to managing these triggers is to keep a diary of what causes your symptoms to flare up, which can help you avoid or mitigate these factors in your daily life.
Common Environmental Triggers Include:
- Sun Exposure: UV rays can damage the skin and cause flare-ups.
- Extreme Temperatures: Both hot and cold weather can exacerbate symptoms.
- Wind: Harsh winds can dry out the skin and increase irritation.
- Stress: Emotional stress can lead to flushing and worsening of symptoms.
- Dietary Factors: Spicy foods, hot drinks, and alcohol are common culprits.
Have you noticed any specific environmental triggers that make your rosacea worse? How do you manage these triggers in your daily life? Share your tips with us!
Immune System Dysfunction: How Does Your Body’s Defense Mechanism Play a Role?
The immune system is your body’s defense mechanism against foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses. However, in people with rosacea, this system can sometimes overreact to certain triggers, leading to inflammation. This overactive immune response is thought to be one of the key factors contributing to the symptoms of rosacea.
Research has shown that certain proteins, known as cathelicidins, which are part of the body’s immune response, are abnormally active in people with rosacea. These proteins can cause blood vessels to dilate, leading to the characteristic redness of rosacea. Moreover, the presence of certain microscopic mites, known as Demodex, on the skin’s surface has been linked to rosacea. These mites are more abundant on the skin of people with rosacea, potentially triggering an immune response that leads to inflammation.
Another factor is the skin’s natural barrier. In people with rosacea, this barrier may be weakened, making it easier for irritants and microbes to penetrate the skin and trigger an immune response. This could explain why people with rosacea often have sensitive skin that reacts strongly to various skincare products and environmental factors.
Key Points About Immune System Dysfunction in Rosacea:
- Overactive Immune Response: Proteins like cathelicidins may be overactive, leading to inflammation.
- Demodex Mites: These microscopic mites may play a role in triggering rosacea symptoms.
- Weakened Skin Barrier: A compromised skin barrier can make the skin more susceptible to irritants.
Do you think your immune system could be playing a role in your rosacea? How do you manage skin sensitivity? Let’s discuss in the comments.
Common Risk Factors: Who Is at Risk of Developing Rosacea?
Now that we’ve explored the causes of rosacea, let’s take a closer look at the risk factors that could increase your chances of developing this condition. While anyone can develop rosacea, certain factors can make it more likely.
- Age and Gender: Rosacea most commonly affects adults between the ages of 30 and 50. It’s also more prevalent in women, although men who develop rosacea tend to experience more severe symptoms.
- Fair Skin: Individuals with fair skin, particularly those of Northern European descent, are more likely to develop rosacea. However, it’s important to note that people with darker skin tones can also be affected, though the symptoms may be less noticeable.
- Family History: As mentioned earlier, having a family history of rosacea or other skin conditions increases your risk. This genetic predisposition suggests that rosacea could run in families.
- History of Blushing or Flushing: People who frequently experience blushing or flushing may be at higher risk of developing rosacea. This could be due to the sensitivity of the blood vessels in the face.
- Sun Exposure: Chronic sun exposure can damage the skin and increase the likelihood of developing rosacea. This makes sun protection a key preventative measure.
- Lifestyle Factors: Stress, alcohol consumption, and a diet high in spicy foods and hot beverages can all contribute to the development and exacerbation of rosacea symptoms.
Summary of Common Risk Factors:
- Age: Most common in adults aged 30-50.
- Gender: More prevalent in women, though men may experience more severe symptoms.
- Skin Type: Fair-skinned individuals are at higher risk.
- Family History: A strong indicator of potential risk.
- Lifestyle: Stress, diet, and alcohol consumption can worsen symptoms.
Do any of these risk factors apply to you? If so, how do you plan to manage your risk? Let's chat about it!
Conclusion: Understanding Rosacea to Manage It Better
Rosacea is a complex condition influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, environmental triggers, and immune system dysfunction. By understanding the causes and risk factors, you can take proactive steps to manage your symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Whether it's avoiding known triggers, protecting your skin from the sun, or maintaining a healthy diet, there are several strategies you can adopt to keep your rosacea under control.
Remember, while rosacea can be challenging, it’s not something you have to face alone. There are many resources and communities out there that can offer support and advice. If you’ve found any strategies that work for you, please share them in the comments below. Your experience could help others who are struggling with the same condition.
If you’re interested in learning more about rosacea and how to manage it, continue reading about the different treatment options and lifestyle changes that can make a difference in your skin health.
What’s one change you can make today to better manage your rosacea? Share your thoughts in the comments!
Resources
American Academy of Dermatology. (2019). American Academy of Dermatology | American Academy of Dermatology. Aad.org. https://www.aad.org/
Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. (2018). Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology Home Page. Jaad.org. https://www.jaad.org/
Mayo Clinic. (2024). Mayo Clinic. Mayoclinic.org; Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. https://www.mayoclinic.org/
National Rosacea Society. (2019). National Rosacea Society. Rosacea.org - National Rosacea Society. https://www.rosacea.org/
WebMD. (2023). WebMD - Better information. Better health. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/
What's Your Reaction?




















